
Due to their proven benefits for mental and physical health, particularly sleep quality, magnesium supplements have become increasingly popular in recent years. Many swear to their calming effect, which is also said to reduce stress and anxiety.
What is Magnesium
Magnesium is a mineral cofactor essential for over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including:
- protein synthesis
- muscle and nerve function
- blood glucose control
- blood pressure regulation
- energy production, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis
Bananas, nuts, pumpkin seeds, and dark green leafy vegetables are common dietary sources of magnesium. Magnesium is also found in fish, poultry, beef, and fortified cereals.

Several dietary surveys and epidemiologic studies revealed that, on average, people's dietary magnesium intake is lower than the Recommended Daily Allowance (RaDA) of 320 to 420 mg/day.
This may be attributed to increased consumption of processed foods, which are commonly low in nutritional value.
Magnesium Supplements
Doctors often recommend magnesium supplements, especially for individuals with specific health conditions or dietary deficiencies.
Forms of Magnesium Supplements
There are several types of magnesium supplements in the market:
- Magnesium Citrate: A popular choice due to its good absorption rate and potential laxative effect, making it useful for occasional constipation relief.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Known for its calming properties, it may help improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety. It's generally well-tolerated and has a lower risk of digestive side effects.
- Magnesium Oxide: A common and affordable option, magnesium oxide has the lowest bioavailability compared to other forms. It may cause digestive upset in some individuals.
- Magnesium Malate: This form is combined with malic acid, which may help alleviate muscle pain and fatigue. It's often used by athletes and individuals with conditions like fibromyalgia.
- Magnesium L-Threonate: Specifically designed to cross the blood-brain barrier, it may improve cognitive function, memory, and sleep.
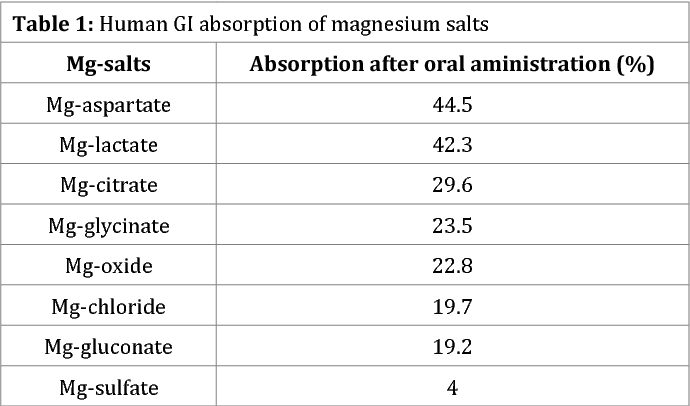
Bioavailability of Magnesium Supplements
Not all forms are equal in bioavailability. The citrate form is the most bioavailable, while the sulfate form is the least.
My Experience with Magnesium Supplement
Due to my unrelenting depressive episodes, I wanted to find relief, aside from my meds through supplements. I came across several Reddit posts claiming that magnesium supplements seemed to alleviate their mental disorders. They reported a decrease in depressive episodes and relief from their anxiety.
This seemed promising, so I bought a bottle of magnesium glycinate tablets ASAP! My depression at that time made me too lazy to cook healthy meals, so it should be a win for me anyway to take a supplement as I am lacking in my diet.
I took 400 mg of Magnesium Glycinate every night before sleep. After a month of taking them, here is what I experienced:
- I slept like a baby! I experienced deep sleep and always woke up feeling refreshed in the morning.
- My brain fog lessened. I can think more clearly; my thoughts are more coherent.
- My depressive episodes have lessened. My suicidal tendencies are gone.
- I have more energy for the day. The depression fatigue is not as intense anymore.
Overall, I can say that magnesium supplement really works for your body's benefit. The effects on sleep and depression are big for me, so I kept taking them until now.
Should I take them?
It doesn't hurt to take them even if you are not clinically deficient. However, it is always recommended that you get this nutrient in your diet. To avoid deficiency, you should aim to eat more veggies, nuts, and seeds.
You may not need to supplement magnesium if you eat a healthy diet. If not, you should take at least 200-400 mg of magnesium daily.
John is a medical scientist with a strong passion for science. He has a strong background in scientific research, gained through numerous clinical internships. John loves to explain medical information in a simple yet informational way to help readers optimize their health.
Leave a Reply